Researchers from the University of Bologna and the University of Padua discovered that lava tubes under the Moon and Mars are 1,000 times larger than those found on Earth. The team measured the tubes found on Earth and compared them to those underneath the other planet.
According to Daily Mail, scientists studied the cavities that lava created billions of years ago under the surface of Mars and the Moon, which can shield them from cosmic radiations. However, due to lesser gravity and the impact the moon had on lava flows, lava tubes found on the Moon are larger than those discovered on Mars or Earth.
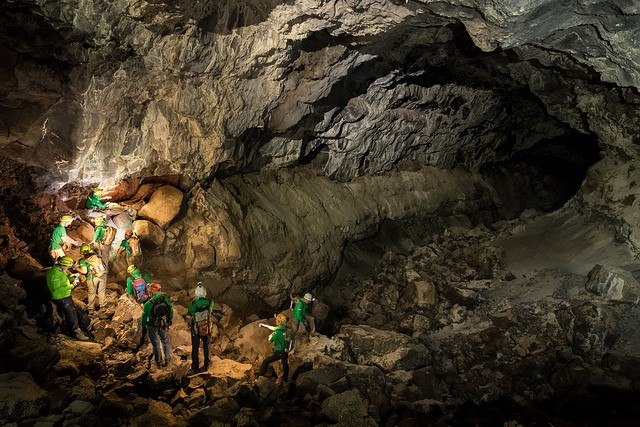

An expedition of astronauts, planetary scientists and engineers collect samples in a lava tube in Lanzarote, Spain. Like on Mars and on the Moon, some of the caves are large enough to accommodate streets. Being underground structures, they are good shelters from radiation. They may contain subsurface water, and therefore be interesting in the search of extraterrestrial microbial life. Pangaea-X is a test campaign that brings together geology, high-tech survey equipment and space exploration. For five days in November 2017, the course mobilised 50 people, f
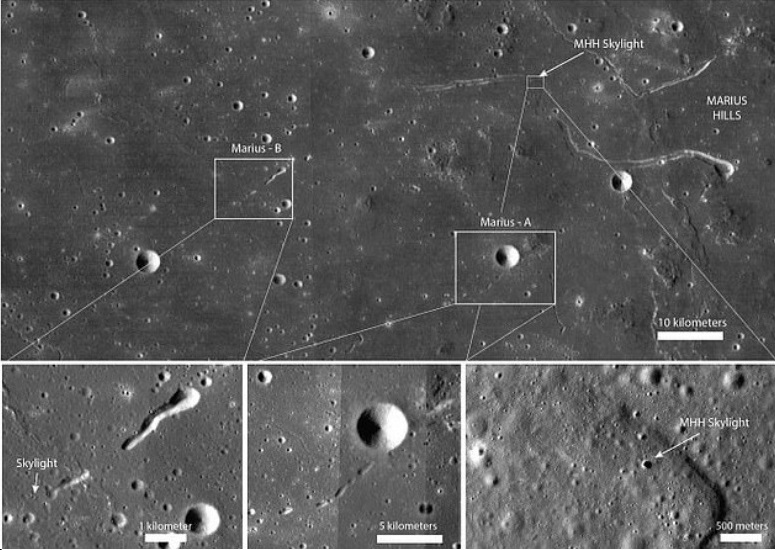
Among those found in the moon, the largest tubes measure more than 25 miles long and up to 100 feet wide. Scientists claimed these lava tubes can accommodate the entire planetary bases for space missions in the future.
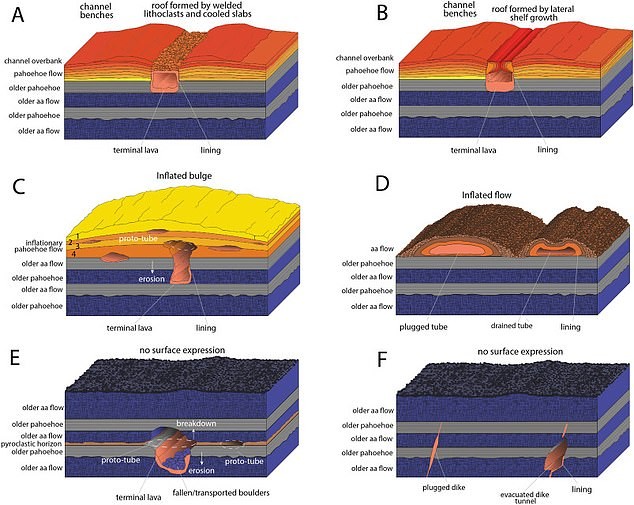
According to the study that was published in the Earth-Science Reviews journal, these lava tubes on the surface of the Moon and Mars are similar to those found in Hawaii, Canary Islands, and Australia. "We measured the size and gathered the morphology of lunar and Martian collapse chains (collapsed lava tubes), using digital terrain models," said Pozzobon adding that the findings are used to estimate the size, shape, and scale of the tubes on other celestial bodies.
European Space Agency (ESA) Francesco Sauro teamed up with planetary geologist Riccardo Pozzobon from the University of Padua to measure their scale.
Martian and Lunar Lava Tubes Are 1,000 times Larger Than Those On Earth, Study Shows
Sauro explained how they found the lava tubes on planet Earth as well as on the subsurface of Moon and Mars using the high-resolution pictures taken by interplanetary probes. He also said that lava tubes are often inferred by examining linear cavities and the locations of sinuous collapse chains taken from satellite images and laser altimetry devices from different probes.
They compared this information to topographic data "about similar collapse chains on the Earth's surface" as well as to laser scans of the lava tubes in Lanzarote and the Galapagos.
Read also: NASA's Juno Mission at Jupiter Reveals Clouds With Ammonia-Water Solution Leading to Unexpected Electrical Discharge
The lava tubes in Mars and the Moon
After years of study, researchers found that lava tubes from on the moon and on Mars are respectively 1,000 and 100 times wider than those on Earth where tubes typically measure up to 98 feet. This huge size difference is due to lower gravity, which affected the early volcanism in these sites.
Meanwhile, the University of Padua researcher Matteo Massironi noted that despite the massive lunar tubes, they are kept within the roof stability threshold due to the lower gravitational attraction. Thus, "the majority of lava tubes underneath the maria smooth plains" remain complete.
Sauro also said that various projects and design challenges have been happening worldwide to create safe designs that will be used for colonizing other worlds like 3D printed materials from lunar regolith as well as the beehive-like structure design that would block radiation and meteorites.
The ESA scientists noted space agencies' special interest in planetary caves and lava tubes, which they regard as the first step towards future moon explorations. These may also lead to a new perspective in planetary exploration.