
As cloud services become more popular, companies are beginning to realize how difficult it is to allocate, track, and optimize cloud costs. They go for reserved capacity to reduce their cloud bills and then get themselves locked in with cloud vendors.
But there is another way to build a flexible and cost-effective cloud setup: spot instances. Sure, the cloud vendor might pull the plug on your instance at any time. But if you take these few steps, there's no need to worry.
Read on to find out how to handle spot instances and snatch high-performing EC2 instance types at a fraction of the cost.
What you need to know about spot instances
-
Let's start with the most important thing. Spot instances offer cost savings up to 90% off the On-Demand price (AWS has several EC2 pricing models, and so do other providers).
-
Spot instances are spare computing resources that might not be available at all times. The amount of available capacity varies significantly depending on size, region, time of day, and a variety of other factors.
-
The availability of spot instances also depends on supply and demand. So, you might experience unexpected behavior if you choose the most popular instance types and an event like Black Friday happens.
-
Before taking your instance back, the cloud vendor notifies you - AWS lets you know about the upcoming interruption 2 minutes before, Azure and Google give you only 30 seconds.
When to use spot instances?
Before jumping on the spot instance bandwagon, make sure that your workload is a good candidate. These questions will point you in the right direction:
-
Does it need a lot of time to finish the job?
-
Is it mission- and time-critical?
-
Is it fault-tolerant?
-
Is it tightly coupled between instance nodes?
-
Do you have a strategy in place for replacing the instance the cloud provider took back?
Here are a few examples of workloads that are good candidates for spot instances:
-
Batch processing jobs
-
Containers and microservices
-
High Performance Computing (HPC) applications
-
CI/CD operations
-
Distributed databases (like Elasticsearch or MongoDB)
-
Any app in an orchestrated environment
Which cloud provider to choose for spot instances?
Amazon Web Services
Product name: Spot Instance
Pricing: Variable and based on demand. The prices are updated every 5 minutes. Check the Spot Instance Advisor for more information.
Support limitations: Maximum 20 spot instances per one AWS Region. This limit is dynamic - new accounts might get less than 20 spot instances and see this limit grow over time.
Also, you might be facing other limits for specific Spot Instance types on your account.
Preemption time: 2 minutes
Maximum time limit: Unlimited (but always depending on the available capacity)
Microsoft Azure
Product name: Spot VM
Pricing: Fixed. You can query pricing information using Azure retail prices API.
Support limitations: Spot VMs don't support sizes in B-series and promo versions of any size (such as Dv2 or NV promo sizes). Also, Spot VMs aren't supported in the region Microsoft Azure China 21Vianet.
Preemption time: 30 seconds
Maximum time limit: Unlimited (depending on the available capacity)
Google Cloud Platform
Product name: Preemptible VM instance
Pricing: Fixed. Take a look at VM instances pricing lists.
Support limitations: GCP can stop a preemptible instance at any time due to system events that depend on current conditions. Also, migrating preemptible instances to regular instances isn't an option.
Preemption time: 30 seconds
Maximum time limit: 24 hours. For some instances, the limit is 6 hours (but you can reset the counter).
How to choose the right spot instance
Take a look around the cloud provider's offer and take your time when shopping for spot instances.
It's smart to choose ones that are slightly less popular because they might run stable for a longer time. They're just less likely to get interrupted.
Always check the frequency of interruption before betting on an instance. This is the rate at which the instance reclaimed its capacity during a given period of time (for example, a month).
AWS displays this information in the Spot Instance Advisor, using ranges of <5%, 5-10%,10-15%,15-20% and >20%:
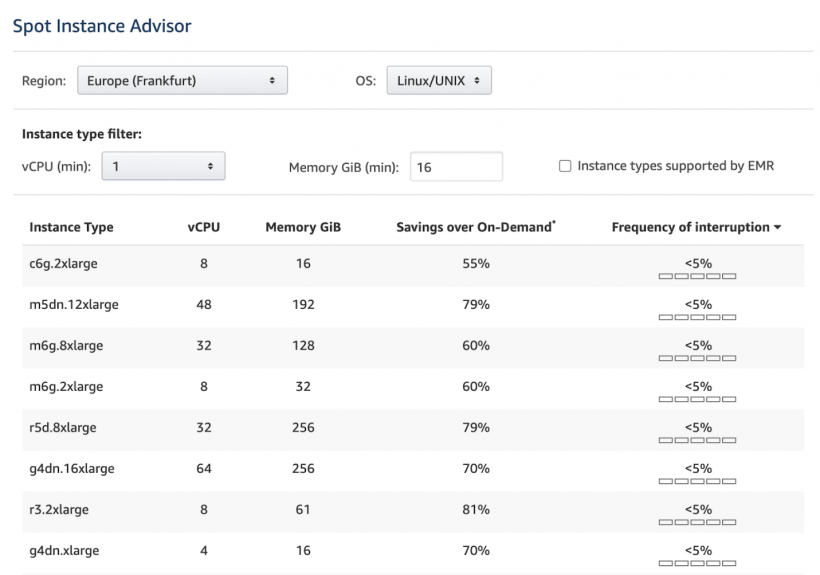
Once you identify a spot instance for your workload, it's time to bid on it. Set the maximum price you're willing to pay for it - the instance will run only as long as your price matches the marketplace rate. To avoid getting interrupted, set your maximum price at the level of the On-Demand pricing.
Manage spot instances in bulk
To increase your chances of grabbing attractive spot instances, you can request multiple instance types at the same time. Also, you get to set a maximum price per hour for the entire fleet, not a specific spot pool (which is a group of instances with the same type, OS, availability zone, and network platform).
Every cloud provider offers this feature:
-
AWS Spot Fleet allows managing a large group of spot instances with different allocation strategies (targeting lowest price or capacity-optimized types, for example).
-
Azure VM scale sets let you create and manage a group of load-balanced VMs, and increase or decrease their number automatically.
-
Google managed instance group brings preemptible instances together after you specify this option in the instance template.
Or automate it all
Downtime from lost spot instances is a serious risk for most companies. You can eliminate this risk and replace instances gracefully by using an automation tool that manages your cloud infrastructure.
Automated cloud management solutions place workloads on spot instances when possible and then automatically fall back to On-Demand instances in case of interruption. Your workload always has a place to run.
* This is a contributed article and this content does not necessarily represent the views of techtimes.com









