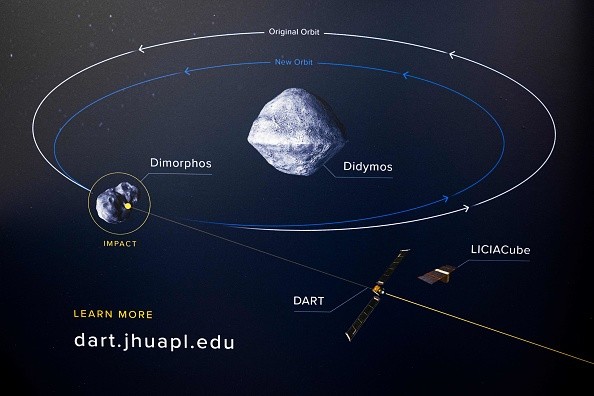
The NASA DART mission made huge headlines after the spacecraft successfully collided with its targeted asteroid, Dimorphos.

For the past few years, the international space union and its partner countries have been making efforts to create technologies that can protect Earth from potential asteroid impacts.
The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) is the most efficient one, as of writing, since it was able to alter the Dimorphos' course.
Scientists revealed that the debris created by the collision assisted the mission's success.
NASA DART Collision Aftermath
According to Space.Com's latest report, scientists shared their estimates on how much debris was created after the DART collision.
They claim that between 2.2 million to 22 million pounds of debris flew off after the satellite crashed on Dimorphos' surface.
However, these millions of pounds of rock particles are just a fraction of the overall mass of the asteroid.
Although this is the case, experts said that the debris still helped DART to change Dimorphos' course.
They explained that if a space rock is hit by a spacecraft without causing any debris, the asteroid will just take the spacecraft's momentum.
But, since the DART mission cause lots of debris, the impact created a beta factor of 3.6. This means that the moment picked up more than three times the momentum.
They added that the debris affected the asteroid more than the NASA DART satellite itself.
"This is very good news for the kinetic impact technique. At least in the case of DART, the kinetic impact on the target was really efficient at changing the orbit of the target," said DART Investigation Team Lead Andy Cheng.
Next Plan for DART Mission
BBC Sky at Night reported that the NASA DART team plans to study how the satellite transferred its energy to Dimorphos.
They already have debris among the major factors that changed the asteroid's momentum. But, more observations are still needed to be conducted.
Scientists said that the best answers could be provided by the upcoming ESA Hera spacecraft, which is scheduled to launch as early as October 2024.
You can click this link to learn more about this new spacecraft.
In other news, the NASA Ingenuity helicopter was able to make its 36th flight on the Red Planet.
We also reported the NASA Artemis 1 Orion capsule finally returned to Earth after a successful lunar orbit.
For more news updates about NASA DART and other advanced satellites, keep your tabs open here at TechTimes.
Related Article : [UPDATE] NASA Successfully Launches Satellite That Could Map All Earth's Water! Here are SWOT Spacecraft's Details

ⓒ 2025 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




