NASA's Quesst mission has rescheduled the first flight of its X-59 quiet supersonic aircraft to 2024. The X-59, a unique experimental aircraft, required intricate engineering collaboration between NASA researchers and prime contractor Lockheed Martin Skunk Works.
It combines cutting-edge technology with systems and components from established aircraft, including its landing gear from an F-16 and life-support system adapted from an F-15.
Technical challenges surfaced during the development phase in 2023, prompting the need for extra time. Hence, integrating systems and resolving intermittent issues with safety-redundant computers controlling the aircraft's systems are underway.
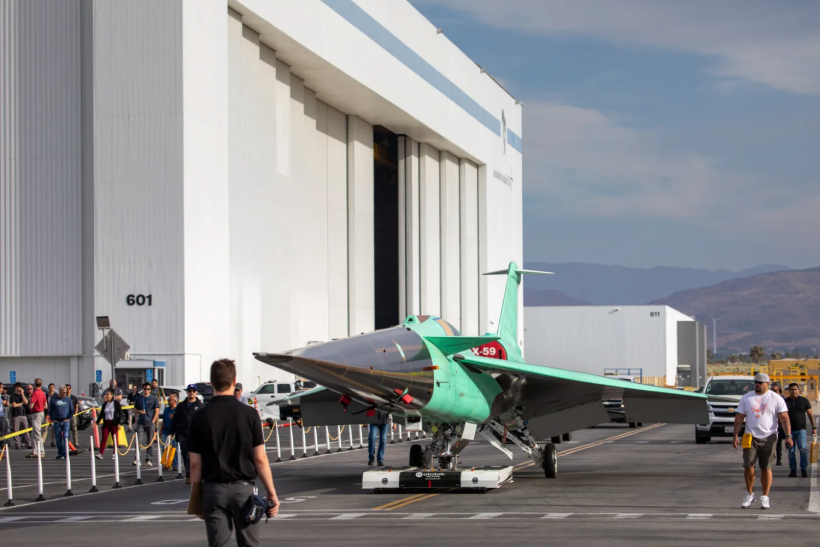

NASA's X-59 research aircraft transitioned from its construction site to the flight line, which denotes the area between the hangar and the runway at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California on June 16, 2023. This relocation facilitated essential safety and structural testing, marking significant progress towards its inaugural flight.
NASA Quesst Mission's Progress
NASA reported that over the past year, Quesst had made significant progress. The team completed the tail structure, finalized electrical wiring, conducted critical ground tests, and transitioned the aircraft to the flight line for structural testing.
The X-59's mission aims to demonstrate supersonic flight while minimizing the typically loud sonic boom to a quieter thump. NASA intends to fly the X-59 over various communities to collect data on public perception of its sound.
This information will be shared with US and international regulators, potentially leading to adjustments in rules currently restricting commercial supersonic flight over land.
The mission's safety and success are NASA's paramount concerns. It entails ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of the X-59, especially during the community test phase. Integrated testing is underway, followed by a flight readiness review, after which NASA will provide a more specific timeline for the maiden flight.
The Quesst mission aims to revolutionize commercial aviation by significantly reducing travel time. The safe and reliable flight of the X-59 is pivotal for achieving these benefits. NASA said it is dedicated to a meticulous review and testing process to ensure mission success.
NASA Quesst Mission's Primary Objectives
The Quesst mission has two primary objectives. First, to design and construct NASA's X-59 research aircraft, which incorporates technology to diminish the loudness of a sonic boom to a gentler thump for ground observers.
Second, to fly the X-59 over various US communities, collecting data on human reactions to the sound produced during supersonic flight. This dataset will be furnished to US and international regulators.
With this data, new regulations pertaining to supersonic flight over land can be formulated and adopted, potentially opening avenues for new commercial cargo and passenger markets offering supersonic air travel.
The components of NASA's Quesst mission are part of two aeronautics programs: the Advanced Air Vehicles Program and the Integrated Aviation Systems Program.
Oversight for the mission is provided by a systems project office that involves members from both programs and all four of NASA's aeronautical research field centers.
These encompass Langley Research Center in Virginia, Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, as well as Ames Research Center and Armstrong Flight Research Center, both in California.
Related Article: Ring Nebula Comes Into Focus: NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Unveils Remains of a Dying Star in Stunning Detail