NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), a spacecraft that has been exploring the planet for a long time, recently captured an intriguing image of sand dunes with remarkably round shapes using its High-Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRise) camera.
HiRise has previously taken pictures of dunes with more typical crescent shapes. Mars' dusty, sandy, and windy environment makes it ideal for sand dune formation.
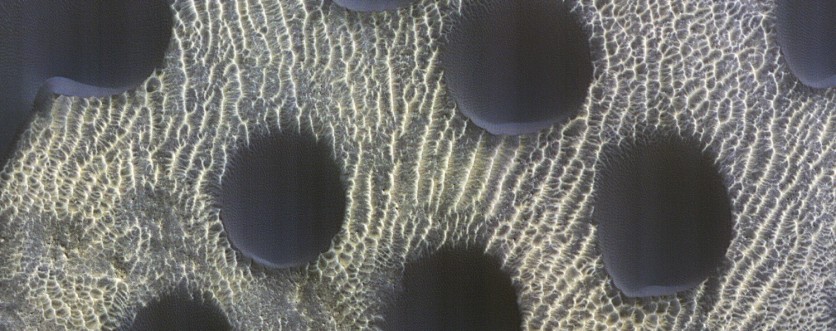
Upon closer inspection, the dunes in the photo are not perfectly circular, but their shape is still notable. Overall, this photo is yet another fascinating glimpse into the unique geological features of Mars.
"Sand dunes of many shapes and sizes are common on Mars. In this example, the dunes are almost perfectly circular, which is unusual," planetary geologist Alfred McEwen wrote for a HiRise picture-of-the-day feature on Thursday, March 2.
"They are still slightly asymmetrical, with steep slip faces on the south ends. This indicates that sand generally moves to the south, but the winds may be variable."
Read Also : NASA Perseverance Rover's MEDA Sensor Damaged by Mars Rocks-Reducing Its Efficiency! Can It Still Be Used?
Seasonal Changes
Using the HiRise camera operated by the University of Arizona, the MRO captured an image of the sand dunes in late November last year.
The purpose of the activity was to monitor seasonal changes in frost coverage. The picture reveals the absence of frost in the surrounding landscape, providing useful information for scientists studying Mars.
MRO has been orbiting Mars since 2006. The mission's primary goal is to investigate the Martian surface, atmosphere, and geology, with the aim of finding evidence of water and possible signs of the past or present life.
The MRO has six scientific instruments on board, including a camera that can take high-resolution images of the planet's surface, a spectrometer that can analyze the composition of rocks and soil, and a radar that can penetrate beneath the surface to reveal geological features.
The MRO has made numerous discoveries, including the detection of water ice beneath the surface and the identification of potential landing sites for future Mars missions.
NASA is interested in exploring Mars for several reasons. One of the main reasons is to better understand the history and evolution of our solar system. Mars is a rocky planet that shares many similarities with Earth and studying its geology, atmosphere, and climate can provide insights into how planets form and evolve over time.
Scientists believe that Mars may have had conditions suitable for microbial life in the past, and the search for signs of life on the red planet is a major scientific goal for many Mars missions.
This explains why NASA and other space agencies have a deep interest in this red planet
Related Article : NASA Perseverance Rover Troubled by Mars Rocks; Operators Say It's Difficult To Find the Right Samples

ⓒ 2026 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




