Kentucky is set to welcome a new recycling facility dedicated to shredding electric vehicle (EV) batteries in a collaborative effort between American and South Korean companies.
The $65 million project, a partnership between US-based Ascend Elements, SK ecoplant, and electronic-waste recycling subsidiary TES, aims to bolster the supply chain for battery-related operations in the same region.
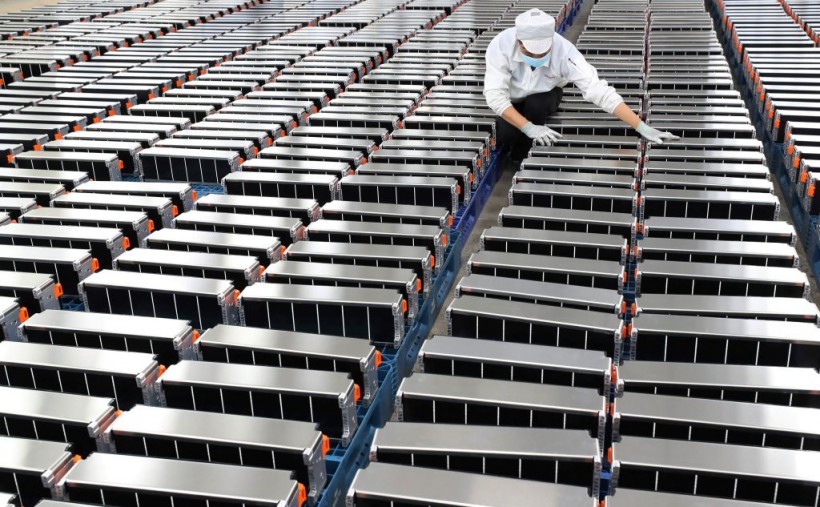

This photo taken on March 12, 2021 shows a worker with car batteries at a factory for Xinwangda Electric Vehicle Battery Co. Ltd, which makes lithium batteries for electric cars and other uses, in Nanjing in China's eastern Jiangsu province.
100,000-Square-Foot EV Battery Recycling Facility in Kentucky
Scheduled to commence construction in November and to conclude by January 2025, the 100,000-square-foot EV battery recycling facility in Hopkinsville, Kentucky, will generate around 60 employment opportunities.
This endeavor marks the inception of a burgeoning industry within the United States, as stated by Mike O'Kronley, CEO of Ascend Elements. He emphasized the necessity of establishing battery recycling facilities in tandem with constructing new EV battery gigafactories.
"This is just the beginning of an entirely new industry in the United States. For every new EV battery gigafactory that is built, we will need to build a new battery recycling facility to process manufacturing scrap and end-of-life batteries," O'Kronley said in a press statement.
"This is a capital intensive endeavor, so joint ventures between strategically aligned partners is an ideal way to fund new infrastructure projects," he added.
This facility will specialize in disassembling and shredding about 24,000 metric tons of used EV batteries and gigafactory scrap every year. To put this into perspective, this equates to processing around 56,000 EV batteries each year.
Moreover, the facility is expected to produce approximately 12,000 metric tons of black mass annually. The black mass is a finely powdered substance containing vital cathode and anode materials found in an EV battery.
The produced black mass will serve as a crucial supply source for Ascend Elements' nearby Apex 1 engineered battery materials facility. This parallel venture, a $1 billion undertaking, is also under construction in Hopkinsville.
Read Also: SolarEV City: Researchers Suggest Combining Solar Power With EVs in Lighting Up Cities Like Paris
pCAM and CAM
When it commences operations in 2024, Apex 1 will stand as North America's inaugural sustainable cathode precursor (pCAM) and cathode active material (CAM) manufacturing facility.
At full capacity, it is projected to furnish sufficient pCAM to support roughly 750,000 new EVs annually. The unique aspect of Ascend Elements' approach lies in its eco-efficient method of producing sustainable pCAM and CAM from black mass.
This patented Hydro-to-Cathode direct precursor synthesis process eliminates multiple intermediary stages in the traditional cathode manufacturing process. Furthermore, this approach yields notable economic and carbon reduction benefits.
The company also claims that several peer-reviewed studies have substantiated that Ascend Elements' recycled battery materials exhibit performance similar to materials derived from virgin sources, all while curbing carbon emissions by up to 93%.
Related Article: Lexus Unveils First All-Electric RZ 450e, Beginning Transforming Into All-electric Brand: Here's What it Offers