
Jeff Bezos, Amazon and Blue Origin founder, has received backing from NASA to upgrade New Shepard, a suborbital spaceship, for future experiments on lunar levels of gravity.
One of the biggest challenges is to five people and systems an opportunity to work on conditions of reduced gravity. The adjustment for astronauts can help them train survivability, and too many systems designed for Earth might misfunction if bought elsewhere. Up-to-date, it has been hard to find training conditions for the space exploration of people.
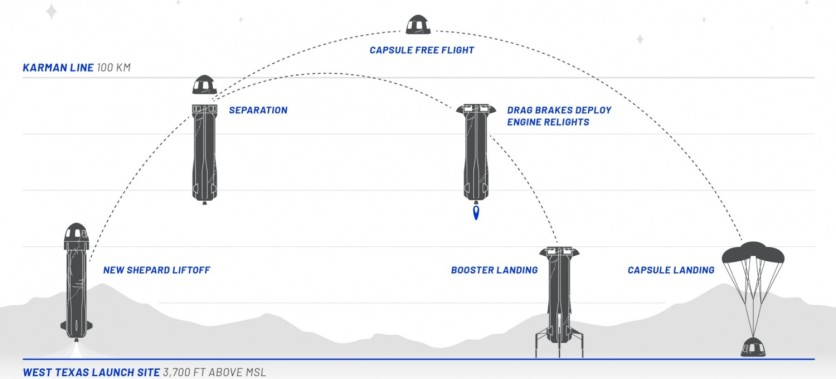
Blue Origin created the spacecraft New Shepard that has created a spectrum of reduced-gravity environments. It experiences up to 17% of the Earth's gravity during its flight, roughly the same gravitational force people and payloads might experience on the moon.
These similar gravity levels are produced on parabolic-flight aircraft using centrifuges on the suborbital craft. These methods, however, have their limits. During a parabolic flight, the lunar gravity experience lasts only by a few seconds, and the centrifuges only accommodate a limited amount of payload.
The New Shepard Subortbital Spacecraft
Blue Origin's method breaks down these limits. The New Shepard capsule goes into a centrifugal about two minutes or more. The capsule has reaction control thrusters that generate a spin of about 11 rotations per minute in a free-fall portion of the flight. The centripetal force produced would be equivalent to the moon's gravity. The whole flight is estimated to take around 11 minutes.
However, Blue Origin's New Shepard has one strong selling point. These crafts under development are all reusable. The 60-foot-tall rocket is designed to accommodate six passengers. Experiencing a gravitational force three times of earth and accelerating to more than Mach 3 speed, you can reach space in a matter of minutes. After a few minutes, you can return to earth as the capsule's parachutes deploy to deliver you a gentle landing.
The reusable aims launch vehicle can take payloads and people easily to space.
Blue Origin continues to conduct its tests on the company's facility in West Texas. Actively researching since 2015, the company has successfully completed crew capsule escape tests at any phase of the flight. Payloads and packages have also successfully been brought to space. With so many successful test runs, the future where people can join a ride to space might be near.
NASA Enlists Itself As The First Customer
An article in Bloomberg says NASA will provide pre-purchase payload space and developmental funds for New Shepard's flights to fund their "new capabilities." This would let them research space conditions of life support, mining, and environmental control systems. The same article says, "NASA purchased a total value of $2.69 million."
NASA provides these supports through their Flight Opportunities program, where you can see Blue Origins as one of the Rocket-Powered Vehicles Supported.
NASA's Artemis program, the plan to send astronauts back to the moon, is scheduled this 2024. With the date coming close, NASA might intensify and invest in their space research with extra intensity. The New Shepard might be the next big step for NASA to get closer to the moon.
Related Article: NASA Hubble Identifies Why Red Hypergiant Star, 300,000 Brighter Than Sun, Suddenly Fades
This article is owned by Tech Times.
Written by Czarina Grace Del Valle
ⓒ 2026 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




